The Science of Brain Rewiring: Techniques to Transform Your Mindset
December 5, 2023
Maximizing Mental Potential: A Guide to Biohacking Your Brain’s Performance
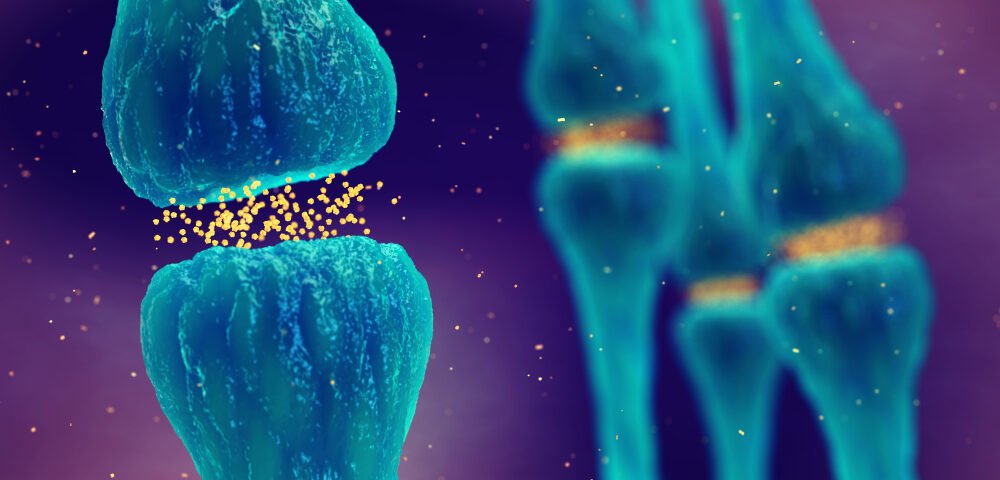
December 5, 2023Neurotransmitters are the brain’s messengers, facilitating communication between neurons and regulating various bodily functions, including mood, cognition, and movement. However, as individuals age or due to certain lifestyle factors, the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain can decline, leading to a range of cognitive and emotional changes.
Effects of Declining Neurotransmitters
When neurotransmitter levels decline, several effects may become noticeable:
Mood Swings and Emotional Changes: Reduced levels of serotonin and dopamine, known as the “feel-good” neurotransmitters, can lead to mood swings, depression, or increased anxiety.
Cognitive Decline: Declining acetylcholine levels are associated with cognitive decline, affecting memory, learning, and overall cognitive function.
Sleep Disturbances: Imbalances in neurotransmitters such as GABA can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia or poor sleep quality.
Reduced Motor Functions: A decrease in dopamine levels can impact motor control and lead to symptoms like tremors or slowed movements.
Solutions to Address Neurotransmitter Decline
Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients, vitamins, and minerals supports neurotransmitter production. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and amino acids (found in protein-rich foods) can aid in maintaining optimal neurotransmitter levels.
Regular Exercise: Physical activity boosts neurotransmitter production and release, especially serotonin and dopamine, promoting better mood and cognitive function.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can deplete neurotransmitters. Practices like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises help reduce stress levels, preserving neurotransmitter balance.
Supplements and Medications: In some cases, supplements or medications prescribed by healthcare professionals can help replenish neurotransmitter levels. These may include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for serotonin imbalances or medications that increase dopamine levels for specific conditions.
Adequate Sleep: Prioritize quality sleep as it supports neurotransmitter production and helps maintain optimal brain function.
Mental Stimulation: Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, such as puzzles, reading, or learning new skills, can help maintain neurotransmitter levels and cognitive function.
Professional Support: Consulting a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or a neurologist, can provide personalized guidance and treatment options based on individual needs and specific neurotransmitter imbalances.
Wrap-up
While a decline in neurotransmitter levels is a natural part of aging, certain lifestyle changes and interventions can help mitigate its effects. Adopting a holistic approach that encompasses a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, adequate sleep, and seeking professional guidance when needed can significantly support and maintain optimal neurotransmitter levels.
Understanding the importance of neurotransmitters and taking proactive steps to support their levels is crucial for overall brain health and cognitive function, promoting a more fulfilling and vibrant life, regardless of age.